
Does Linux have a recycle bin?

Recovering files is a great feature that every operating system’s File Manager offers users. In the case of Linux, you can access the File Manager and the Terminal, where you can perform file or folder deletion. Thus, you may be doubtful whether Linux offers the capability to recover files when deleted using a File Manager or the Terminal.
Does Linux have a recycle bin? Linux has a recycle bin that you can access through the File Manager, such as Nautilus or the Terminal. To access the recycle bin, open the default File Manager of your Linux Window Management System. On the sidebar, you will find the Trash, Rubbish bin, or WasteBasket, where deleted files and directories are stored. Thus, you may restore or delete the files or directories permanently. However, files deleted using the rm command are not recycled on Linux.
One can use two approaches to delete files and directories on Linux: Delete files permanently or move them to the recycle bin temporarily.
How to delete files on Linux using the File Manager
While using the File Manager to delete files and directories, you can delete them permanently or move them to the recycle. Depending on the File Manager you may be using, moving the files to the recycle bin is the default method of deleting files. A common File Manager on Linux is the Nautilus or Gnome File Manager.
To access the files stored in the recycle bin, follow these steps:
How to access the recycle bin on Linux using the File Manager
Step 1: Open your favorite File Manager on Linux
You may search ‘File Manager’ in the Apps list to access the File Manager on Linux.
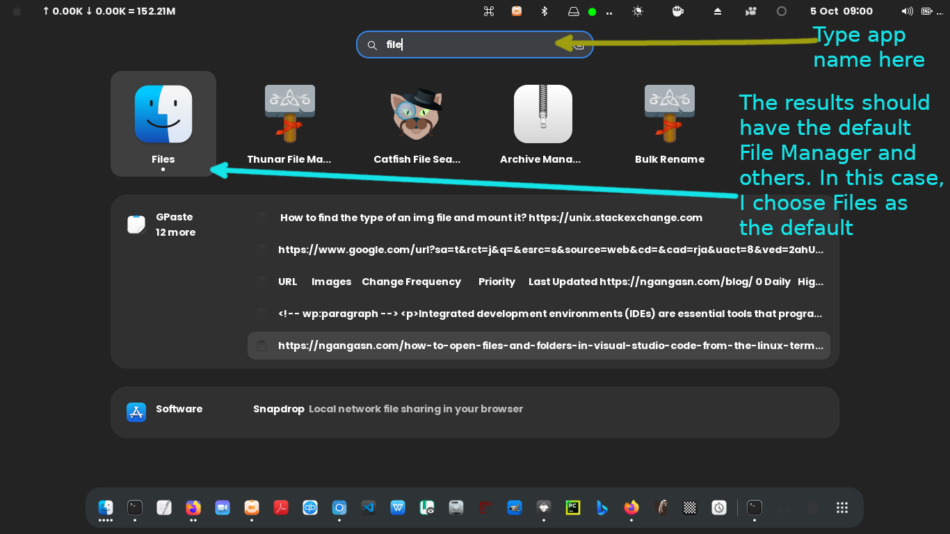
Alternatively, you may find the File Manager pinned on the Dock, as shown below.
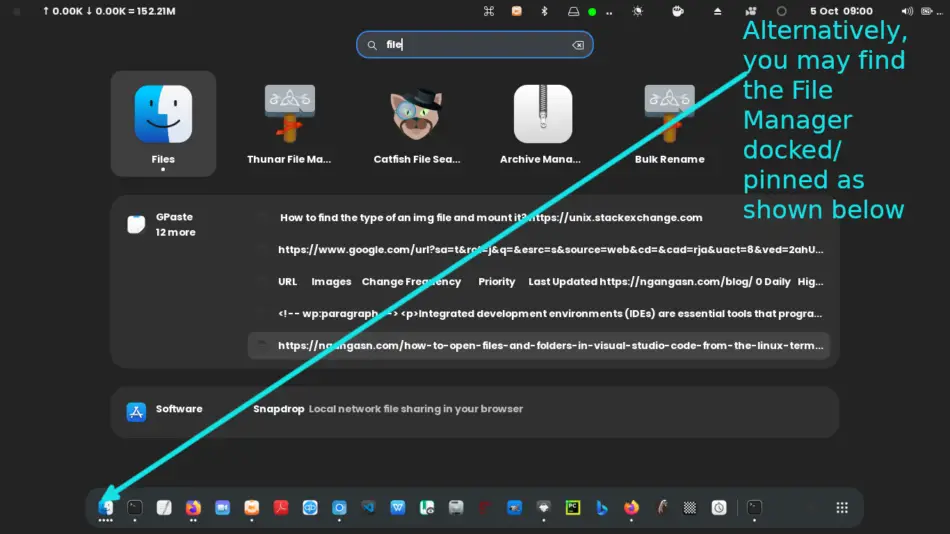
Besides, you can access your File Manager through the Terminal by typing its binary name. For example, Gnome File Manager’s binary name is the nautilus. Thus, to open Gnome File Manager using the Terminal, type the following command on the Terminal and hit Enter.
nautilusA new File Manager window should open, displaying the contents of the user’s home folder or the working directory on the Terminal.
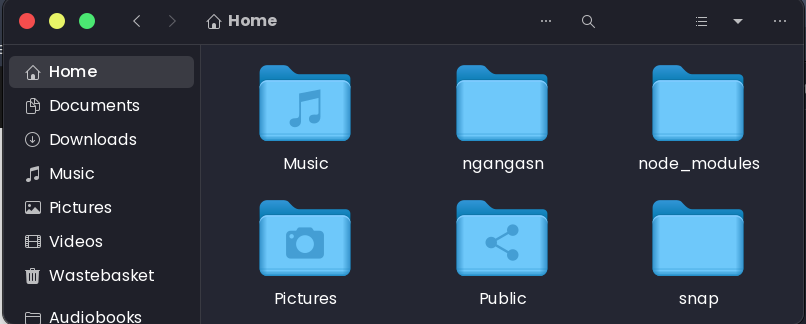
Step 2: Access the trash/waste/recycle bin folder
Using the GUI window of the File Manager, you will find the recycle bin folder named either Trash, WasteBasket, or Recycle Bin on Linux. Inside the directory, you will find all the files and folders you had previously deleted using the File Manager or trash-cli program.
You will find the WasteBasket/Trash/Rubbish Bin directory pinned on the left pane.
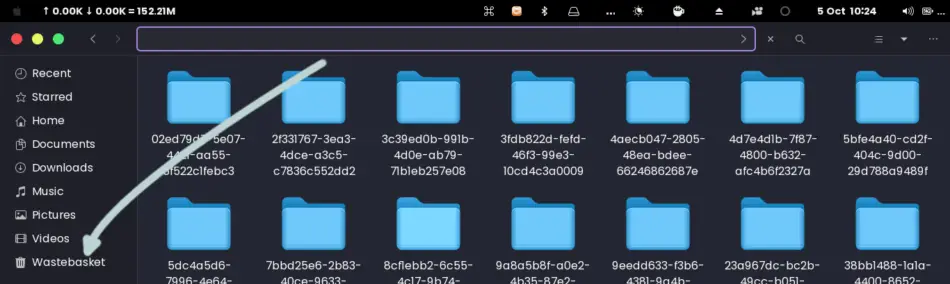
Inside the directory, you will find all the files and directories you had previously deleted.
Besides, you will find other options such as Restore, Empty, and Settings.
You can recover your files by using the Restore button. To recover all files, highlight all the files by pressing CTRL + A and pressing the Restore button. To recover one file or a couple of files, highlight the files by pressing CTRL and left-click on the files you want to restore. Then, press the Restore button to recover the files.
You can delete all the items in the recycle bin by pressing the Empty button. The option will delete the files in the recycle bin permanently. Thus, you may not be able to recover the files later.
You may also press the Settings button to access more recycle bin capabilities. Here, you may set the recycle bin emptying process automatic, automatic deletion of temporary files, and set the time to empty the files.
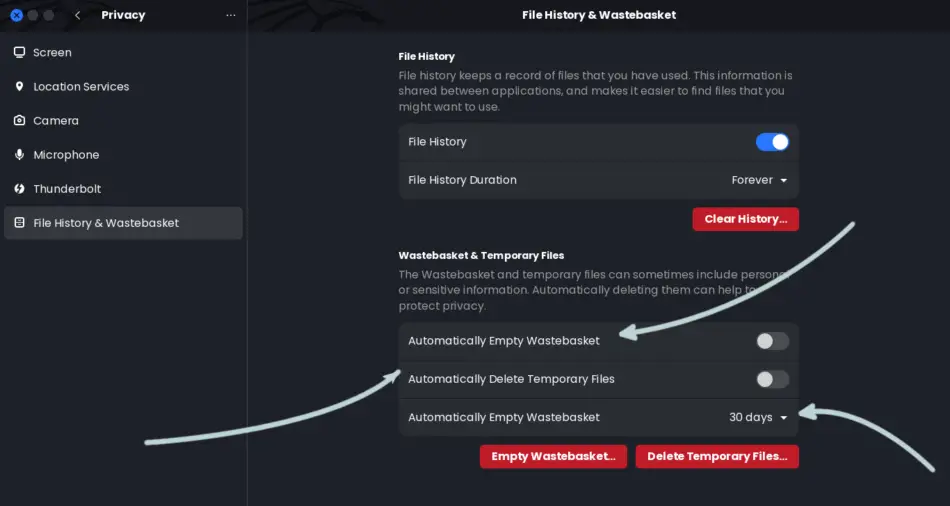
An alternative method of accessing recycle bin on Linux involves using the Terminal.
How to access the recycle bin on Linux using the Terminal
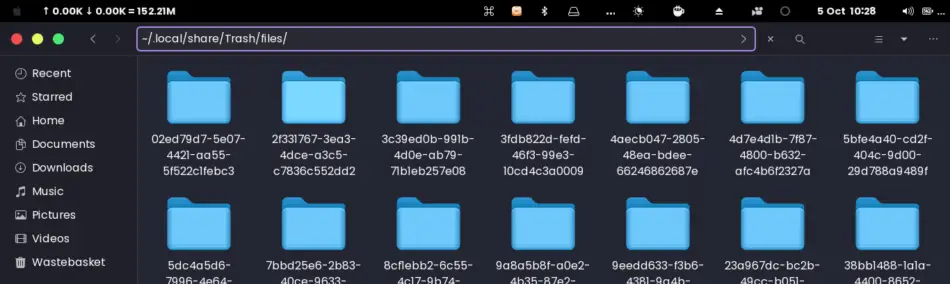
You may also access deleted files and directories by using the Terminal. In the Terminal, you may use the cd command to navigate into the recycle bin folder. On Linux, files and folders in the recycle bin are stored inside the ~/.local/share/Trash/files directory.
You can access the directory using the Terminal through the change directory (cd) command. To do that, open the Terminal and type the following:
cd ~/.local/share/Trash/filesThen, you may choose to list the files by using the ls command that displays all your deleted files inside recycle bin folder. To restore the files, you may use the cp command to copy the files to another directory. Alternatively, you may use the mv command to move the files into a separate directory.
If typing the Linux commands on the Terminal may seem tedious, you can copy the path to the Linux recycle bin directory (~/.local/share/Trash/files) and access it using the File Manager.
To open a path using the File Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open File Manager
Step 2: Press / and then delete to leave the input area on top of your File Manager window empty.
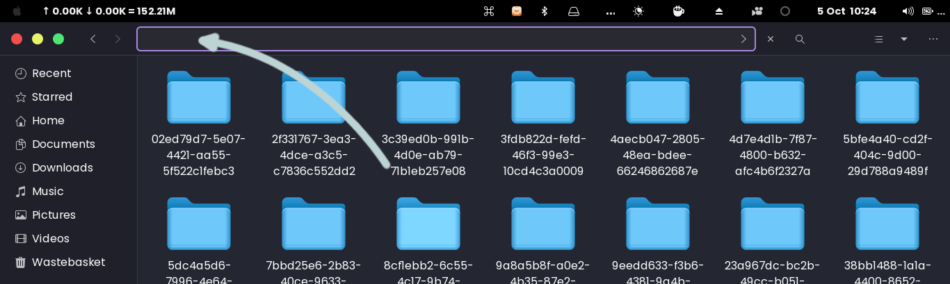
Step 3: Paste the path of the directory. In this case, paste ~/.local/share/Trash/files and press Enter
How to delete files on Linux using the Terminal and move them to the recycle bin
When deleting files on Linux using the rm command, these files are deleted permanently and not moved to the recycle bin. Therefore, if you ever delete your files using the command, you cannot be able to recover them.
Fortunately, the trash-cli tool can help you avoid deleting files and directories permanently. The trash-cli program lets you delete your files on the Terminal by moving them into the recycle bin. Thus, you may recover files later if the need arises.
To delete files using trash-cli on the Terminal on Linux, type trash filename to delete a file.
trash file1.txtTo delete a directory, type trash -d directory_name
trash -d my_old_dirTo delete more than one file, you may use the recursive option through the command trash -r file1.txt file2.txt.
trash -r file1.txt file2.py file.txtBesides, you may delete all the files in the current working directory by using an asterisk with the trash command, trash -r *
trash -r *After deleting the files and directories, you will find all your deleted files inside the recycle bin directory, ~/.local/share/Trash/files, or using the File Manager trash folder. Thus, you can be able to restore these files if you ever need them back.
But first, you must install trash-cli to start using it. Follow these steps to install the program.
How to install trash-cli on Linux
Follow these steps to install trash-cli on Linux.
Open the Terminal and update the system.
Type the following command to update your Linux system:
sudo apt updateType the following command to install trash-cli
For Debian, such as Kali Linux, Ubuntu, e.t.c
sudo apt install trash-cliFor Fedora
sudo dnf install trash-cliFor openSUSE
sudo zypper in trash-cliFor Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S trash-cliThat’s it. You should be able to use the trash command on Linux Terminal to delete your files temporarily.
Related Questions
Where are deleted files in Linux?
Deleted files are stored inside the recycle bin folder on Linux, which is ~/.local/share/Trash/files. However, only files that are deleted temporarily are stored here. Files deleted using the File Manager, or the trash-cli tool can be found in this directory and are recoverable. However, permanently deleted files using the rm command cannot be found in this directory.
You will find deleted files stored in each partition recycle bin directories on Linux, usually named Trash-1000 and $RECYCLE.BIN. To find deleted files for each partition or external media such as an external hard drive or Pendrive, navigate into the drive folder and locate .Trash-1000 and $RECYCLE.BIN directory. The deleted files will be inside /media/username/drivename/.Trash-1000/files.
Does emptying the recycle bin permanently delete files?
Emptying the recycle bin will delete the files and directories stored in the recycle bin permanently. After emptying the recycle bin, you cannot be able to recover the files again.
Conclusion
Linux does have a recycle bin allowing the users to recover their files and directories once the need arises. However, one must be careful while using certain Linux commands such as rm because deleted files cannot be recovered using the recycle bin when used.
Fortunately, Linux provides a File Manager recycle bin and additional tools, such as trash-cli, temporarily allowing Linux users to delete files and folders. Thus, they can delete files and directories using the File Manager and the Terminal while having the option to recover them.

